For a quick and easy start, request free samples.
CSS Do not remove
-
Type 2 diabetes not on insulin

Dexcom G7 15 Day: It’s even a win for patients with type 2 diabetes who do not use insulin2
G7 15 Day can help you redefine their diabetes journey
 Enhanced ease of use and adherence with 15.5-day wear time4
Enhanced ease of use and adherence with 15.5-day wear time4
 Further lower A1C when paired with a GLP-1 agonist†,5
Further lower A1C when paired with a GLP-1 agonist†,5
 Associated with reduced cardiovascular risk in as little as 3 months‡,§,2
Associated with reduced cardiovascular risk in as little as 3 months‡,§,2
Why CGM for adults with type 2 diabetes not on insulin?

ADA guidelines recommend CGM as an option for adult patients with type 2 diabetes whether they use6:
- Insulin
- Non-insulin injectable glucose-lowering medications
- Oral glucose-lowering medications
ONLY 13%
 of patients with TYPE 2 DIABETES have adopted CGM7
of patients with TYPE 2 DIABETES have adopted CGM7A1C=hemoglobin A1C; ADA=American Diabetes Association; ASCVD=atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease; BGM=blood glucose monitoring; CGM=continuous glucose monitoring; CPT=Current Procedural Terminology; DME=durable medical equipment; GLP-1=glucagon-like peptide-1.
*In a retrospective study, diabetes-related hospitalizations reduced 12 months after CGM use: Non-insulin (-31%) Basal insulin (-48%) Prandial insulin (-53%).1 †Retrospective analysis using Optum’s de-identified Clinformatics® database comprised of US administrative claims and linked laboratory data was conducted between 7/1/2018 and 3/31/2023. ‡Results obtained from previous Dexcom device(s). §Cardiovascular risk refers to 10-year ASCVD risk. Visit tools.acc.org/ascvd-risk-estimator-plus to access the American College of Cardiology ASCVD Risk Estimator Plus. ||Based on a person testing blood glucose 5x a day vs. 288 readings using Dexcom CGM. ¶55% of participants surveyed wore Dexcom CGM. #Individual prices may vary depending on insurance coverage. Under Medicare's DME fee schedule, reimbursement and coinsurance for CGMs using CPT codes A4239 and E2103 are the same, regardless of CGM brand.
1 Garg SK, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024;26(11):5202-5210. 2 Reed J, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024;26(7):2881-2889. 3 Shields S, et al. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):31990. 4 Garg SK, et al. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2025;27(6):413-502. 5 Nemlekar P, et al. Am J Manage Care. 2025;31(4):183-188. 6 Diabetes Technology: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2025. Diabetes Care. 2025;48(1 Suppl 1):S146-S166. 7 Mayberry LS, et al. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;38(11):2546-2552. 8 Dexcom G7 15 Day User Guide. 9 Lind N, et al. Diabetes Care. 2024;47(5):881-889. 10 Dexcom G7 User Guide. 11 Ehrhardt N, et al. Clin Diabetes. 2020;38(2):126-131. 12 Cowart K, et al. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2021;18(11):1049-1055.
-
Type 2 diabetes on insulin

Dexcom G7 15 Day: gives your type 2 diabetes patients on insulin more time in range using less insulin.2
2.4% reduction in A1C from baseline at 6 months†,3
Dexcom CGM is clinically proven to lower A1C1
Changes in A1C through 1 year

Study design: Real-world study of 74,679 type 2 diabetes adults, including 1375 basal insulin users and 3122 prandial insulin users. A1C values analyzed pre-index, 3, 6, and 12 months post-index, represented as mean ±SEM. Significant improvements in A1C were observed at 3 months and sustained throughout the study period (‡P<.0001).Key findings in patients with type 2 diabetes on insulin
 Real-world study showed statistically significant A1C reduction at 3 months and sustained at 1 year§,1
Real-world study showed statistically significant A1C reduction at 3 months and sustained at 1 year§,1
 CGM was associated with a reduction in hospitalizations and emergency room visits1
CGM was associated with a reduction in hospitalizations and emergency room visits1
 CGM decreased A1C across all therapy types (BIT and PIT) regardless of medication changes||,1
CGM decreased A1C across all therapy types (BIT and PIT) regardless of medication changes||,1


Even for patients who meet their A1C goals (<7%), CGM provides 24-hour insights to ensure every glucose excursion can be addressed.
Compare glycemic outcomes with CGM vs. BGM in adults with insulin-treated type 2 diabetes2
CGM-derived metrics at baseline and 12-month follow-up.

Study design: A 12-month, single-center, open-label randomized controlled trial comparing CGM with BGM in 76 adults with insulin-treated type 2 diabetes. Participants were randomized 1:1, with the primary outcome being change in time in range (70-180 mg/dL) from baseline to 12 months, measured by blinded CGM. Secondary outcomes included A1C, insulin dose, weight, and patient-reported outcomes (¶P<.05).2
The wins add up every day

+3.6 more hours
in range per day2

"a game changer"
Study participants said Dexcom CGM is “a game changer” for motivating better habits2

2.4% reduction in A1C
from baseline at 6 months†,3
Why CGM for patients with type 2 diabetes on insulin?

ADA guidelines recommend CGM as an option for adult patients with type 2 diabetes whether they use4:
- Insulin
- Non-insulin injectable glucose-lowering medications
- Oral glucose-lowering medications
ONLY 13%
 of patients with TYPE 2 DIABETES have adopted CGM6
of patients with TYPE 2 DIABETES have adopted CGM6CGM reveals dangerous hyper- and hypogylcemic excursions6
Blood glucose monitoring (BGM) doesn’t reveal the full story. CGM provides the complete 24-hour picture to help your patients address spikes or troughs BGM can miss.

Illustrative model of a 24‑hour blood glucose profile; not derived from an actual patient dataset.
A1C=hemoglobin A1C; ADA=American Diabetes Association; BGM=blood glucose monitoring; BIT=basal insulin therapy; CGM=continuous glucose monitoring; CPT=Current Procedural Terminology; DME=durable medical equipment; PIT=prandial insulin therapy; SEM=standard error of mean.
*In a retrospective study, diabetes-related hospitalizations reduced 12 months after CGM use: Non-insulin (-31%) Basal insulin (-48%) Prandial insulin (-53%).1 †After 6 months, for patients with type 2 diabetes who initiated Dexcom CGM in primary care. §This retrospective cohort analysis used Optum's deidentified Market Clarity data of >79 million people to evaluate CGM use in people with type 2 diabetes who were treated with non-insulin (NIT), basal insulin (BIT) and prandial insulin therapy (PIT). ||Retrospective cohort analysis using Optum deidentified Market Clarity data of >79 million people to evaluate CGM use in people with type 2 diabetes. #Individual prices may vary depending on insurance coverage. Under Medicare’s DME fee schedule, reimbursement and coinsurance for CGMs using CPT codes A4239 and E2103 are the same, regardless of CGM brand.
1 Garg SK, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024;26(11):5202-5210. 2 Lind N, et al. Diabetes Care. 2024;47(5):881-889. 3 Grace TP, et al. Clin Diabetes. 2024;42(4):540-546. 4 Diabetes Technology: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2025. Diabetes Care. 2025;48(1 Suppl 1):S146-S166. 5 Mayberry LS, et al. J Gen Intern Med. 2023;38(11):2546-2552. 6 Dexcom G7 15 Day User Guide.
-
Type 1 diabetes

Dexcom G7 15 Day: Increases TIR and lowers A1C in type 1 diabetes2-11
Dexcom G7 15 Day: Proven results in patients with type 1 diabetes12
Compared to BGM, Dexcom CGM demonstrated significant A1C reduction12

Study design: The COMISAIR-2 study was the 3-year follow-up to the COMISAIR trial which compared the efficacy and safety of long-term regimens of sensor-augmented insulin regimen (SAIR) among individuals. This nonrandomized, prospective, real-world, clinical trial followed 94 participants with type 1 diabetes. The primary end point was the difference in A1C groups after 3 years of follow-up.12
Dexcom CGM is simply the most accurate for your patients with type 1 diabetes.†,8,13
Industry-leading accuracy leads to better results:

overall MARD8,13

94.3% of readings
are within clinical accuracy standards14

90.3% accuracy from insertion
consistent from Days 1 to 1514

-0.9% reduction in A1C vs. BGM
in type 1 diabetes in DIAMOND (older adults subanalysis)15

>2.6 hours
more time in range daily§,16

72%reduction in hypoglycemia
and 50%+ reduction in nighttime glycemic events||,17
The evidence is clear: Dexcom CGM is a win in the management of type 1 diabetes
CGM delivers greater A1C reduction, increased time in range, fewer hypoglycemic events, and improved quality of life.5-7,9,17-19
Study/Source Population Key Outcomes (CGM vs. BGM) DIAMOND study Adults with type 1 diabetes (MDI) A1C REDUCTION: -1.0% vs. -0.4%; significant reduction in hypoglycemia¶,5,20 GOLD randomized clinical trial Type 1 diabetes (various ages) Three times as many achieved >1.0% A1C reduction; 80% fewer hypoglycemic events21 COMISAIR study Type 1 diabetes (MDI and pump) A1C improvement depended more on CGM than insulin delivery method12 FLASH-UK trial Adults with type 1 diabetes CGM with alarms led to greater A1C reduction22 Why CGM for patients with type 1 diabetes?

ADA guidelines recommend CGM for all adult patients with type 1 diabetes2:
- On MDI and insulin pumps
- As early as diagnosis
LESS THAN50%
 of patients with TYPE 1 DIABETES have adopted CGM23
of patients with TYPE 1 DIABETES have adopted CGM23CGM reveals dangerous glucose variability.14
Blood glucose monitoring (BGM) doesn’t reveal the full story. CGM provides the complete 24-hour picture to help your patients address spikes or troughs BGM can miss.

Illustrative model of a 24‑hour blood glucose profile; not derived from an actual patient dataset.
A1C=hemoglobin A1C; BGM=blood glucose monitoring; CGM=continuous glucose monitoring; CPT=Current Procedural Terminology; DME=durable medical equipment; MARD=mean absolute relative difference; MDI=multiple daily injections; TIR=time in range.
*In a retrospective study, diabetes-related hospitalizations reduced 12 months after CGM use: Non-insulin (-31%) Basal insulin (-48%) Prandial insulin (-53%).1 †A study was conducted to assess the sensor life where 73.9% of sensors lasted the full 15 days. In other words, when using the product per the package labeling, approximately 26% of sensors may not last for the full 15 days. ‡Adults ≥60 years old. §Time in range increase when comparing users on Dexcom G6 against Sensor Augmented Pump Users. ||Hypoglycemia defined as glucose ≤3.0 mmol/L for ≥20 min. ¶Adults on multiple daily insulin injections. #Individual prices may vary depending on insurance coverage. Under Medicare’s DME fee schedule, reimbursement and coinsurance for CGMs using CPT codes A4239 and E2103 are the same, regardless of CGM brand.
1 Garg SK, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024;26(11):5202-5210. 2 Diabetes Technology: Standards of Care in Diabetes-2025. Diabetes Care. 2025;48(1 Suppl 1):S146-S166. 3 Karakus KE, et al. Diabetes Care 2023;46:1646-1651. 4 Aleppo G, et al.; Diabetes Care 2021;44:2729-2737. 5 Šoupal J, et al. Diabetes Care. 2020;43:37-43. 6 Data on file, (VV-07576). Dexcom, 2025. 7 Garg SK, et al. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2025;27(6):413-502. 8 Dexcom G7 15 Day User Guide. 9 Ruedy KJ, et al. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2017;11(6):1138-1146. 10 Brown SA, et al. N Engl J Med. 2019;381(18):1707-1717. 11 Heinemann L, et al. Lancet. 2018;391(10128):1367-1377. 12 Beck, RW, et al. JAMA. 2017;317(4):371-378. 13 Beck RW, et al. Ann Intern Med. 2017;167(6):365-374. 14 Martens T, et al. JAMA. 2021;325(22):2262-2272. 15 Laffel LM, et al. JAMA. 2020;323(23):2388-2396. 16 Welsh JB, et al. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2024;18(1):143-147. 17 Gilbert TR, et al. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2021;23(S1):S35-S39. 18 Beck RW, et al. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2017;5(9):700-708. 19 Lind M, et al. JAMA. 2017;317(4):379-387. 20 Leelarathna L, et al. N Engl J Med. 2022;387(16):1477-1487. 21 Lacy M, et al. Clin Diabetes. 2024;42(3):388-397.
-
Diabetes during pregnancy

Dexcom G7 15 Day is the only CGM† with proven accuracy and safety in pregnancy2,3
In patients with type 1, type 2, or gestational diabetes4
Diabetes during pregnancy can increase risks for mothers and babies2,3,5-10
Dangers for mothers
 Cesarean delivery5
Cesarean delivery5 Preeclampsia‡,2,3,6-9
Preeclampsia‡,2,3,6-9 Preterm birth‡,2,3,6-9
Preterm birth‡,2,3,6-9Dangers for unborn babies
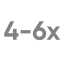 Risk of stillbirth10
Risk of stillbirth10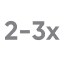 Risk of shoulder dystocia10
Risk of shoulder dystocia10 Risk of large gestational age (LGA)†,2,3,6-9
Risk of large gestational age (LGA)†,2,3,6-9 Less time in the NICU3
Less time in the NICU3
Diabetes can take a toll on expectant mothers’ health11,12
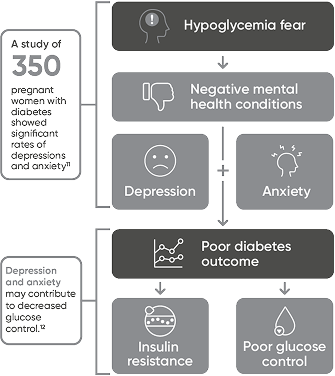
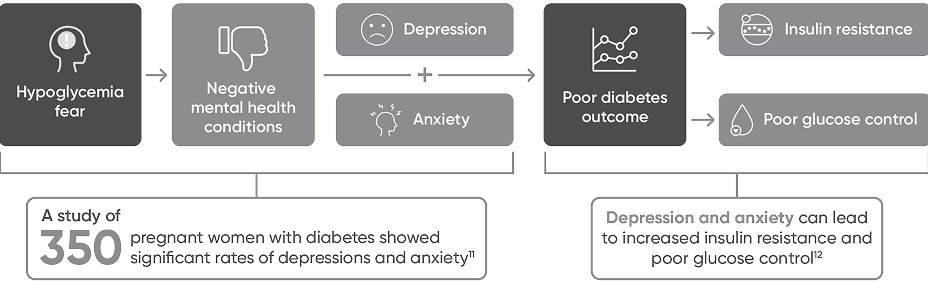

Using Dexcom CGM may help pregnant patients with diabetes achieve better glucose control.2,6-8,13,14
The only CGM† proven safe and accurate for pregnant patients2

of glucose readings
may be missed with BGM§,15

Better glycemic control
by adjusting treatment and lifestyle behaviors, without fingersticks||,2,6-8,13,14

15 days of wear¶,#,16,17
safe and accurate across glucose ranges and pregnancy trimesters2
Why CGM for pregnant patients with diabetes?
CGM provides the complete 24-hour picture to help your patients address spikes or troughs BGM can miss4,18
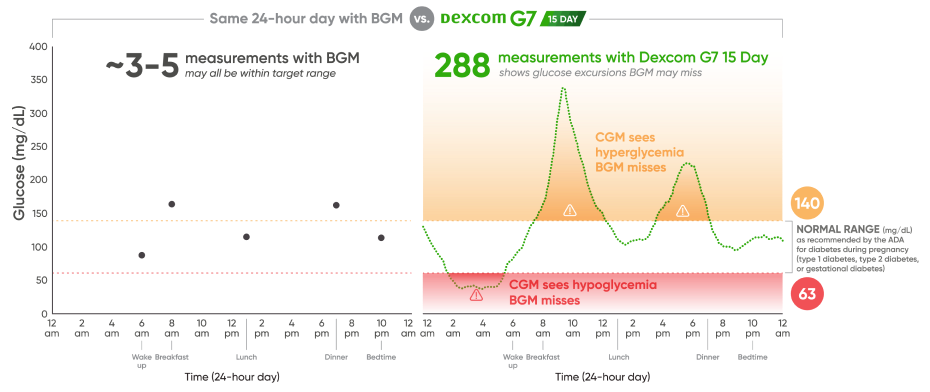
Illustrative model of a 24‑hour blood glucose profile; not derived from an actual patient dataset.

Pregnancy glycemic control goals: Safely increase TIR quickly while reducing glycemic variability.18
Trust the only CGM proven to be safe for pregnant patients with diabetes†,2
Lower risk to the mother
 Hyperglycemia2,14
Hyperglycemia2,14 Preeclampsia†,2,19
Preeclampsia†,2,19 Gestational weight gain‡,14,20
Gestational weight gain‡,14,20 Rate of C-sections‡,2,19
Rate of C-sections‡,2,19Lower risk to the baby
 LGA‡,21
LGA‡,21 Neonatal hypoglycemia21
Neonatal hypoglycemia21 NICU admissions21
NICU admissions21
ADA=American Diabetes Association; BGM=blood glucose monitoring; CGM=continuous glucose monitoring; NICU=neonatal intensive care unit; TIR=time in range.
*In a retrospective study, diabetes-related hospitalizations reduced 12 months after CGM use: Non-insulin (-31%) basal insulin (-48%) prandial insulin (-53%).1 †Based on commercially available CGMs that have completed clinical trials evaluating accuracy and safety in pregnant patients with diabetes. ‡Studies have demonstrated an association between elevated glucose and increased incidence of cesarean delivery, preeclampsia and birth weight >90th percentile. §Based on a person testing blood glucose 5x a day vs. 288 readings using Dexcom CGM. ||Fingersticks required for diabetes treatment decisions if symptoms or expectations do not match readings.4 ¶A study was conducted to assess the sensor life where 73.9% of sensors lasted the full 15 days. In other words, when using the product per the package labeling, approximately 26% of sensors may not last for the full 15 days. #Excludes implantable CGM systems. **Individual pricing may vary depending on commercial insurance coverage.
1 Garg SK, et al. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2024;26(11):5202-5210. 2 Polsky S, et al. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2024;26(5):307-312. 3 Hapo Study Cooperative Research Group, et al. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(19):1991-2002. 4 Dexcom G7 15 Day User Guide. 5 Gonzalez-Quintero VH, et al. Diabetes Care. 2007;30(3):467-470. 6 The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. Obstet Gynecol. 2018;131(2):e49-e64. 7 Beck RW, et al. JAMA. 2017;317(4):371-378. 8 Beck RW, et al. Ann Intern Med. 2017;167(6):365-374. 9 Welsh JB, et al. J Diabetes Sci Technol. 2024;18(1):143-147. 10 Hussain SA, et al. Case Rep Obstet Gynecol. 2020;8142109:1-5. 11 Salimi HR, et al. Diabetes Epidemiol Manage. 2024. 12 OuYang H, et al. J Diabetes Res. 2021;995779:1-10. 13 American Diabetes Association. Standards of Care in Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2023;46:S1-S291. 14 Feig DS. Diabetes Care. 2022;45(11):2484-2491. 15 Dexcom G7 User Guide. 16 Data on file (VV-07561). Dexcom; 2025. 17 Data on file (VV-07558). Dexcom; 2025. 18 Battelino T, et al. Diabetes Care 2019;42:1593-1516. 19 Yu F, et al. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(12):4674-4682. 20 Wei Q, et al. Sci Rep. 2016;6:19920. 21 Murphy HR. Diabetologia. 2019;62(7):1123-1128.
MAT-11235






